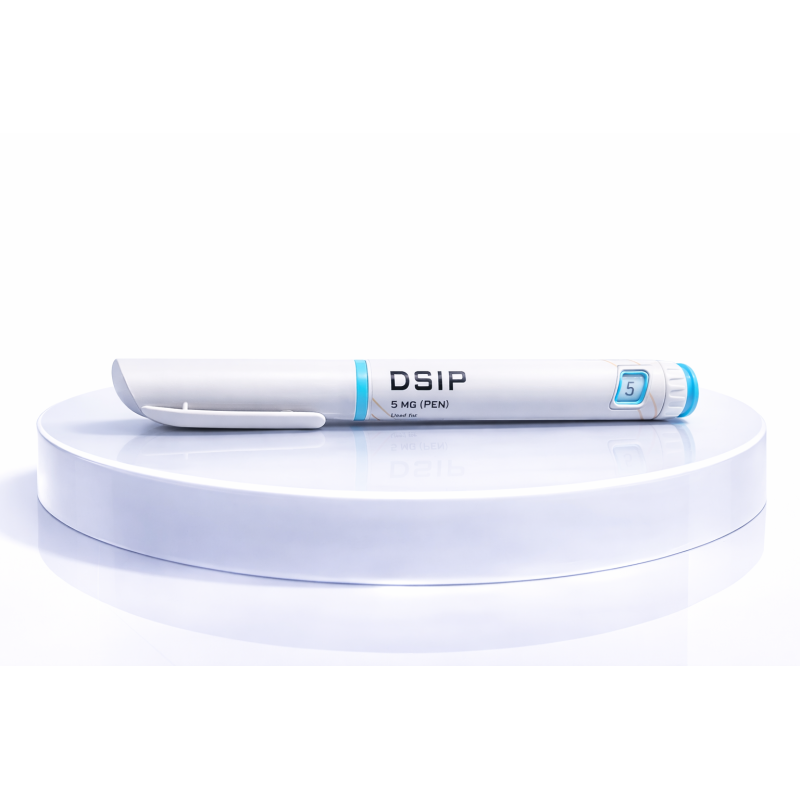


DSIP (Delta Sleep Inducing Peptide) supports deep sleep and hormonal balance. Useful for athletes and people who suffer from overtraining or stress. Improves recovery and overall sense of vitality.
- 0%
- 0%
- 0%
- 0%
- 0%
Report this review.
This substance alters when and how deeply a person sleeps and how the body responds to stress by affecting the internal communication between the brain and other organs.
What is DSIP
Within research on the regulation of sleep and stress responses, neuronal peptides represent a key component in modulating brain rhythms and hormonal axes; in this context DSIP (delta‑sleep‑inducing peptide) has been studied as a small neuropeptide with a potential role in increasing slow-wave sleep and modulating stress-related axes.
Mechanism of action
Available data suggest that DSIP affects both central and peripheral processes: modulation of electrophysiological patterns in the hypothalamus and brainstem, alteration of the release of certain neurotransmitters, and regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis; the exact receptor mechanism remains partly unidentified, and the effects are likely mediated through a series of intermediate signaling pathways and local interactions with enzymes and receptor systems. This leads to observed changes in EEG slow-wave activity and in the secretion of certain hormones.
| Study | Model | Number | Duration | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classical preclinical EEG analysis | Rat | n=12 | Acute infusion | Increase in slow-wave sleep ~25–35% compared to control |
| Small clinical observation | Healthy volunteers | n=10 | Single administration | Change in sleep architecture with variable results; the data are preliminary |
| In vitro enzyme stability | Plasma/serum | pilot samples | in vitro | Rapid proteolytic degradation; limited biostability |
Research applications and pharmacokinetics
DSIP is studied in fields such as the neurophysiology of sleep, endocrine regulation, and peptide pharmacology; the available experiments are controlled and mostly preclinical. Short biological stability is observed, with data showing rapid proteolytic degradation in blood, which is relevant for experimental design and interpretation of results; human pharmacokinetic data are limited and preliminary.
Sources and review materials: DSIP, PubMed: reviews and articles on DSIP, PubMed: experimental EEG studies.
Formula: C35H48N10O15
The text is intended for educational and research purposes only.